Introduction
In today’s digital world, protecting your personal information has never been more critical. Every click, every app download, and every online transaction leaves traces of your private data. From email addresses and phone numbers to banking details and social media activity, your personal data is valuable—and it can easily fall into the wrong hands. That’s why learning personal data protection tips is essential for everyone, whether you are a beginner just getting online or someone who frequently uses digital services.
Personal data breaches are no longer rare. Cybercriminals constantly seek opportunities to steal sensitive information for financial gain, identity theft, or even blackmail. Fortunately, there are practical steps you can take to secure your digital presence. By understanding how to protect your personal information, you can minimize risks, enjoy the internet safely, and maintain control over your private life.
What is Personal Data Protection?
Personal data protection refers to the process of securing your personal information from unauthorized access, misuse, or theft. It includes practices and tools designed to keep sensitive information—such as your name, email, phone number, financial data, passwords, and even location—safe from cyber threats.
In simpler terms, personal data protection is about controlling who can see or use your information and how it is handled. It’s not just about online safety; it extends to any platform where your data exists, including emails, mobile apps, cloud storage, and social networks.
The main goal is to prevent unauthorized individuals or organizations from misusing your personal information. This includes cybercriminals, hackers, and even companies that may collect more information than necessary. Effective personal data protection ensures your privacy, reduces the risk of identity theft, and gives you peace of mind in a connected world.
Why is Personal Data Protection Important?
Personal data protection is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevent Identity Theft
Identity theft occurs when someone uses your personal information to commit fraud. This can include opening bank accounts, applying for loans, or making purchases in your name. Protecting your data reduces this risk significantly. - Protect Financial Information
Sensitive financial data, like credit card numbers and bank account details, are prime targets for hackers. Personal data protection ensures that your money and financial reputation remain secure. - Maintain Online Privacy
Every time you share information online, it can be tracked or sold to third parties. Data protection helps you control who sees your data and prevents unwanted surveillance. - Avoid Social Engineering Scams
Scammers often use personal information to manipulate or deceive people. By safeguarding your data, you make it harder for criminals to trick you. - Comply with Laws and Regulations
Many countries have strict data protection laws. Protecting your personal information ensures you comply with regulations and avoid legal complications.
In short, personal data protection is not just a precaution; it is a necessity for safe online engagement.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
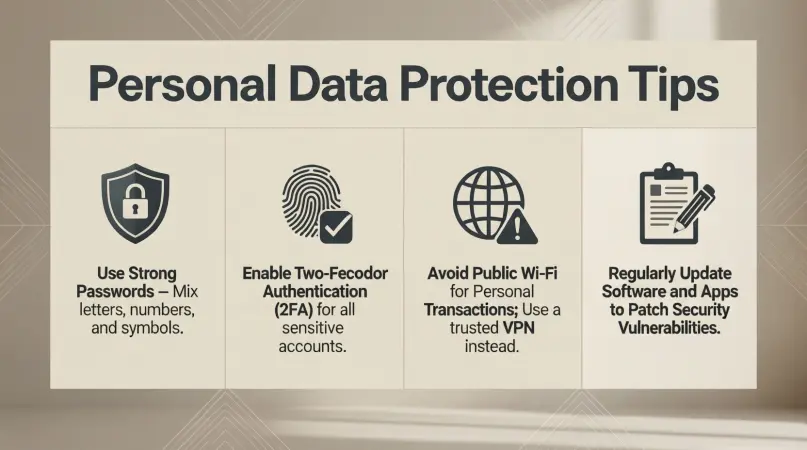
Step 1: Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Passwords are the first line of defense for personal data protection. Avoid simple or common passwords like “123456” or “password.”
Tips:
- Use a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Create unique passwords for each account.
- Use a password manager to securely store and generate passwords.
Example: Instead of “John123,” use “J0hn!R&2026$” for stronger security.
Step 2: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, usually a code sent to your phone or email.
Benefits:
- Even if a hacker steals your password, they cannot access your account without the 2FA code.
- Many online services, including email, banking apps, and social media, offer 2FA.
Step 3: Keep Software and Devices Updated
Outdated software and devices can have security vulnerabilities. Hackers often exploit these weaknesses to steal personal data.
Tips:
- Regularly update your operating system, apps, and antivirus software.
- Enable automatic updates to ensure you don’t miss critical patches.
Step 4: Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easier for attackers to intercept data.
Tips:
- Avoid logging into sensitive accounts on public Wi-Fi.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet connection.
- Turn off automatic Wi-Fi connections on your devices.
Step 5: Limit Sharing of Personal Information
Be mindful of what you share online. Social media platforms and online forms often ask for unnecessary details.
Tips:
- Avoid sharing sensitive information like your full address, birth date, or financial details.
- Review privacy settings on social networks to control who can see your data.
Step 6: Secure Your Emails
Email accounts are gateways to many other accounts. Protecting them is essential.
Tips:
- Avoid clicking suspicious links or attachments.
- Use spam filters and report phishing attempts.
- Change your email passwords regularly.
Step 7: Encrypt Sensitive Files
Encryption converts your data into a secure format that only authorized users can read.
Tips:
- Encrypt sensitive documents before storing them on your computer or cloud.
- Many operating systems offer built-in encryption tools.
- Consider using encrypted messaging apps for communication.
Step 8: Regularly Backup Your Data
Backing up data ensures you can recover it if it’s lost or compromised.
Tips:
- Use external hard drives or secure cloud services for backups.
- Schedule automatic backups to avoid forgetting.
- Keep multiple backup copies in different locations.
Step 9: Monitor Your Accounts
Regular monitoring helps detect unusual activity early.
Tips:
- Check bank and credit card statements regularly.
- Set up alerts for account logins and transactions.
- Use credit monitoring services to track identity theft.
Step 10: Educate Yourself About Cyber Threats
Awareness is key to personal data protection. Cyber threats constantly evolve, and staying informed helps you adapt.
Tips:
- Follow cybersecurity news and blogs.
- Learn to recognize phishing emails and scam tactics.
- Share knowledge with family and friends to protect them as well.
Benefits of Personal Data Protection
- Enhanced Privacy: Your personal information remains confidential.
- Financial Security: Reduces the risk of theft or fraud.
- Peace of Mind: Less worry about cyber threats or scams.
- Control Over Data: You decide who can access your information.
- Legal Compliance: Meets privacy and data protection regulations.
- Better Online Experience: Safer browsing and transactions.
Disadvantages / Risks
- Time-Consuming: Implementing security measures can take time.
- Cost: Some tools, like premium VPNs or password managers, may require payment.
- False Sense of Security: Even with precautions, no system is 100% safe.
- Limited Access Convenience: Stronger security may make logging in slower or more complex.
- Over-Reliance on Technology: Users may neglect common sense practices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Ignoring software updates or security patches.
- Clicking links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
- Oversharing personal information on social media.
- Failing to backup data regularly.
- Ignoring 2FA options offered by services.
- Assuming public Wi-Fi is safe for sensitive transactions.
FAQs
1. What is the easiest way to protect my personal data online?
The easiest method is to use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication for all accounts. These basic steps provide a robust first layer of protection.
2. Is using a VPN necessary for personal data protection?
Yes, especially on public Wi-Fi. A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it harder for hackers to intercept your data.
3. How can I tell if my data has been compromised?
Signs include unusual account activity, unknown transactions, password reset notifications, or alerts from credit monitoring services.
4. Are free password managers safe to use?
Some are secure, but paid options usually offer better encryption and features. Always research before using any password manager.
5. Can I protect my data without technology tools?
Yes, by practicing good habits such as avoiding oversharing, being cautious with emails, and using strong, memorable passwords. Technology tools enhance security but are not the only solution.
6. How often should I update my passwords?
Ideally, every 3–6 months for sensitive accounts. Immediate updates are necessary if you suspect a breach.
7. Is encrypting my files really necessary?
If you store sensitive information, encryption adds a critical layer of security. It ensures that even if your files are stolen, they cannot be read without the encryption key.
8. Can personal data protection prevent identity theft completely?
No system is foolproof, but strong personal data protection significantly reduces the likelihood of identity theft. Regular monitoring and good practices are essential.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Use Biometric Security: Fingerprint or facial recognition adds extra protection.
- Avoid Default Security Questions: Use unique answers that are not easily guessable.
- Limit Third-Party App Access: Only grant permissions necessary for functionality.
- Delete Unused Accounts: Old accounts can be exploited if neglected.
- Educate Children About Online Safety: Protect your family by teaching safe digital practices.
- Check Privacy Policies: Know how services handle and store your data.
- Regularly Clear Cookies and Cache: Reduces tracking and potential leaks.
- Consider Identity Theft Insurance: Extra security for high-risk individuals.
Conclusion
Protecting personal data is no longer optional—it’s a fundamental part of living in a digital world. From preventing identity theft to ensuring financial security, the benefits of robust personal data protection tips are immense. Implementing strong passwords, two-factor authentication, encrypted storage, and mindful online behavior can safeguard your information and give you peace of mind.
While technology tools like VPNs, password managers, and encryption software help, personal responsibility plays a crucial role. Avoiding common mistakes, monitoring accounts, and staying informed about cyber threats ensures you remain one step ahead of potential dangers.





